Turbocharger vs supercharger is a classic debate in the automotive world that pits two formidable technologies against each other, both designed to boost engine performance. Forced induction systems have evolved significantly over the years, allowing drivers to experience more power and efficiency from their vehicles. Understanding how these systems work, their historical context, and the advantages they offer can help you choose the right option for your ride.
Turbochargers and superchargers both compress air to increase engine power, but they do so in different ways. Turbochargers use exhaust gases to spin a turbine, while superchargers are mechanically driven by the engine itself. As we delve deeper into their operations, benefits, and impact on performance, it becomes clear how these technologies have shaped modern automotive engineering.
Introduction to Forced Induction
Forced induction is a crucial concept in automotive engineering that significantly enhances engine performance. By compressing the intake air, it allows for more fuel to be burned in the combustion chamber, leading to increased power output. Two primary types of forced induction systems are turbochargers and superchargers, each utilizing different methods to achieve this goal. Historically, forced induction systems have evolved from early automotive experiments to the sophisticated technologies we see in modern vehicles, providing a means to achieve more power without increasing engine size.
Concept of Forced Induction
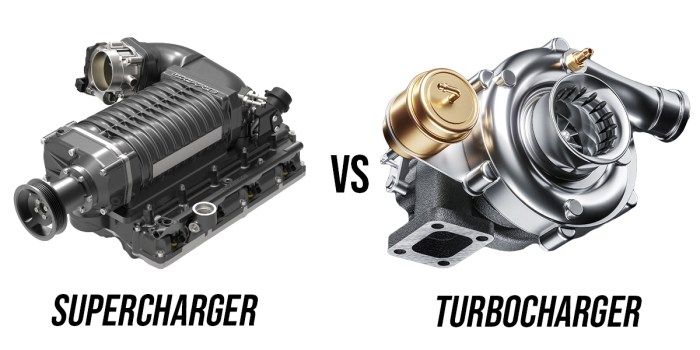
Forced induction systems work by forcing more air into the engine than it would normally draw from atmospheric pressure alone. This process is achieved through:
- Turbochargers: Utilizing exhaust gases to spin a turbine connected to a compressor, which then forces more air into the engine.
- Superchargers: Driven directly by the engine’s crankshaft, they compress air before it enters the combustion chamber.
Over the years, these systems have developed from simple add-ons to integral components of high-performance vehicles, reflecting significant advancements in technology and engineering practices.
Turbocharger Overview
Turbochargers consist of several key components, each playing a vital role in their operation. At the core of the turbocharger is the turbine and compressor setup, along with various other parts that contribute to its efficiency and effectiveness.
Components of a Turbocharger, Turbocharger vs supercharger
The main components of a turbocharger include:
- Turbine Wheel: Spins due to exhaust gases, creating the necessary energy to operate the compressor.
- Compressor Wheel: Compresses incoming air before it enters the engine’s intake.
- Center Housing: Contains bearings that support the turbine and compressor, allowing for smooth rotation.
- Wastegate: Regulates exhaust flow to maintain optimal boost pressure.
The process of air compression in a turbocharger occurs when exhaust gases flow through the turbine, causing it to rotate. This rotation drives the compressor, which draws in and compresses air, leading to increased power output.
Benefits of Turbochargers
Modern vehicles equipped with turbochargers enjoy several advantages:
- Increased Power Output: Turbocharging allows smaller engines to produce more power, enhancing performance without increasing engine size.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: By optimizing air-fuel mixtures, turbochargers can lead to better fuel economy.
- Reduced Emissions: More efficient combustion results in lower emissions compared to naturally aspirated engines.
The effectiveness of turbochargers makes them a popular choice among manufacturers looking to balance power and efficiency.
Supercharger Overview

Superchargers differ from turbochargers in their operational mechanics and design. They provide an immediate boost in power by directly compressing air before it enters the engine.
Types of Superchargers
There are various types of superchargers, each with unique characteristics:
- Roots Supercharger: Features two rotors that pull in air and push it into the engine, providing instant boost.
- Centrifugal Supercharger: Uses a belt-driven impeller to compress air, similar to a turbocharger but powered by the engine’s crankshaft.
These types of superchargers are commonly used in high-performance vehicles, providing immediate throttle response and enhanced performance.
Operation of Superchargers
Superchargers work by compressing air and pushing it into the engine’s intake manifold. This additional air allows for more fuel to enter the combustion chamber, resulting in a higher power output.
Vehicles like the Ford Mustang and Chevrolet Corvette often utilize superchargers, showcasing significant gains in horsepower and acceleration.
Comparison of Turbochargers and Superchargers

A detailed comparison between turbochargers and superchargers illustrates their respective advantages and disadvantages. Below is a table summarizing key differences:
| Feature | Turbocharger | Supercharger |
|---|---|---|
| Power Delivery | Delayed response (turbo lag) | Immediate response |
| Efficiency | More efficient, uses exhaust gases | Less efficient, draws power directly from engine |
| Weight | Typically lighter | Usually heavier |
| Maintenance | Requires more upkeep | Generally easier to maintain |
The choice between a turbocharger and a supercharger depends on the intended use of the vehicle and driving conditions. While turbochargers excel in efficiency, superchargers offer immediate power, making each suitable for different applications.
Performance Implications
Both turbochargers and superchargers significantly improve engine performance by increasing horsepower and torque output. The results can be striking, as shown in various case studies.
Case Studies of Vehicle Performance
Many enthusiasts have documented vehicle performance before and after the installation of forced induction systems. Notable examples include:
- Nissan 370Z: After turbocharging, typical horsepower increased from 332 to over 500.
- Chevrolet Camaro: Adding a supercharger can boost power output from 275 to 450 horsepower.
When integrating either system, tuning considerations must be taken into account to optimize performance and ensure engine longevity.
Fuel Efficiency and Emissions
Turbochargers and superchargers both influence fuel efficiency in distinct ways. Turbocharging often leads to better fuel economy, while supercharging can increase fuel consumption due to its direct drive nature.
Emissions Profiles Comparison
Vehicles equipped with turbochargers typically emit fewer pollutants compared to those with superchargers. This efficiency is attributed to the more complete combustion of fuel facilitated by the additional air provided by turbochargers.
To minimize emissions while utilizing forced induction, manufacturers are adopting advanced technologies and tuning strategies.
Installation and Upgrades
Installing a turbocharger or supercharger involves several steps to ensure proper functionality and compatibility with the engine.
Installation Process Overview
A general installation process includes:
- Disconnecting the battery and removing the existing intake system.
- Mounting the turbocharger or supercharger to the engine.
- Connecting all necessary piping and hoses for air and coolant.
- Integrating a new fuel management system if needed.
- Final checks and tuning for optimal performance.
Safety precautions, such as using protective gear and ensuring a clean work environment, are critical during installation. Proper tools like wrenches, torque wrenches, and hose clamps are essential for a successful upgrade.
Future Trends in Forced Induction Technology: Turbocharger Vs Supercharger
Emerging technologies in turbocharging and supercharging hold the promise of enhanced performance and efficiency.
Hybrid Systems
Innovations such as hybrid systems that combine both turbocharging and supercharging are gaining traction. These systems aim to leverage the immediate power of supercharging with the efficiency of turbocharging, potentially revolutionizing performance vehicles.
As manufacturers continue to explore advancements in efficiency and performance, the future of forced induction technology looks promising, paving the way for more powerful and environmentally friendly vehicles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the turbocharger vs supercharger debate reveals a lot about personal driving preferences and vehicle applications. Each system has its unique advantages and drawbacks, depending on factors like efficiency, power delivery, and engine longevity. As technology continues to advance, there’s no doubt that forced induction will play an even more significant role in the future of performance vehicles, making it an exciting time for car enthusiasts.